
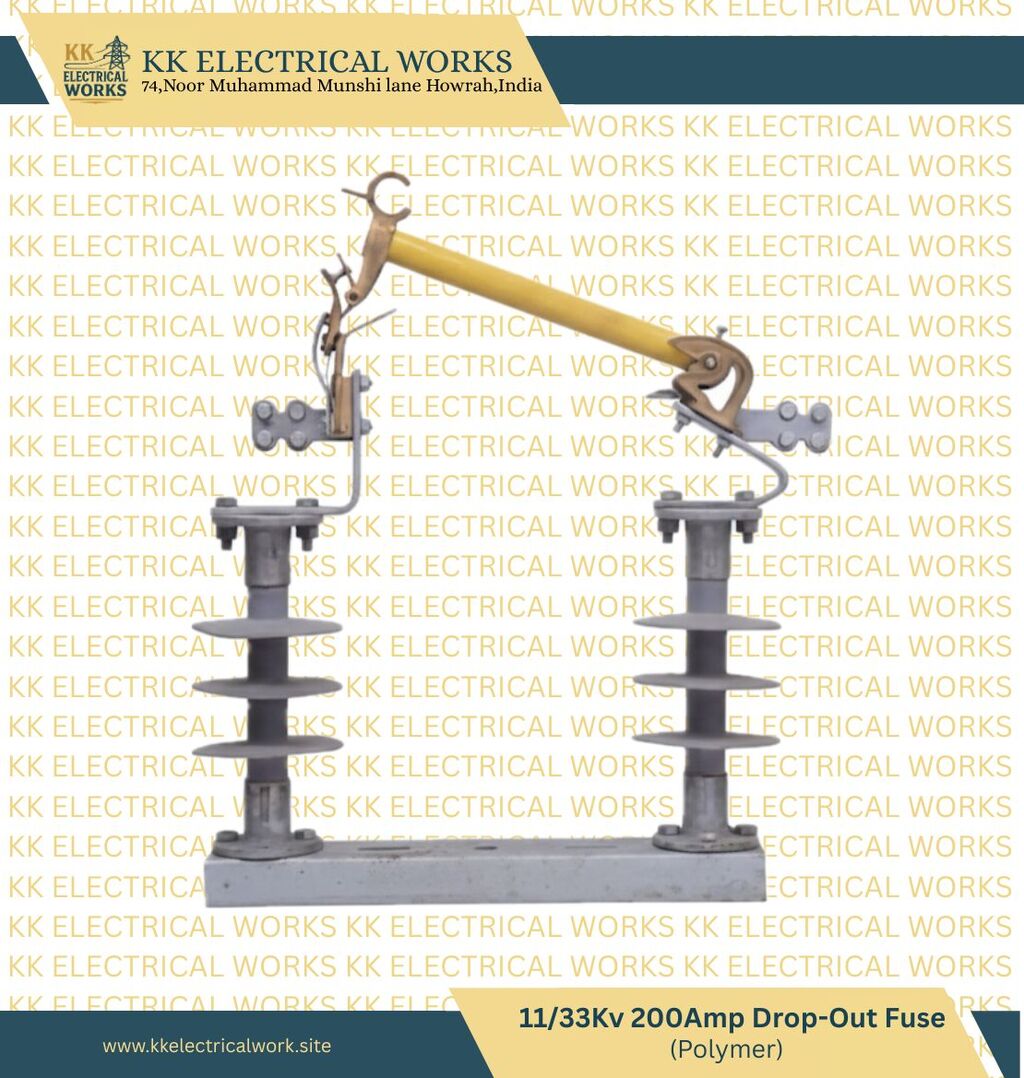
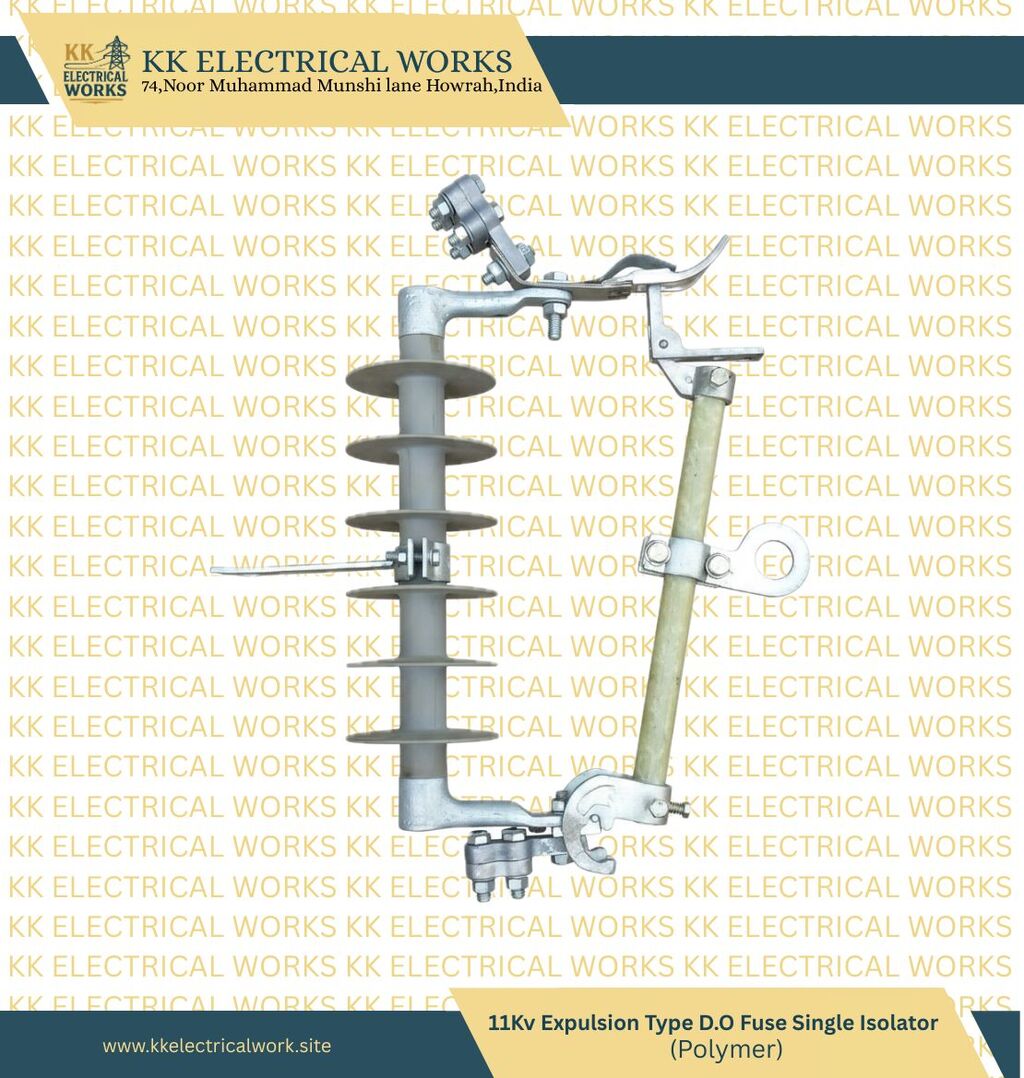








A Drop-Out Fuse (DOF), also commonly referred to as an expulsion fuse or fuse cutout, is a crucial safety device used primarily in high-voltage overhead power distribution systems. Its main function is to protect distribution transformers, feeder lines, and other equipment from damage caused by overloads and short circuits. The device consists of a fuse element housed within a fuse tube (or carrier) that is mounted on a non-conductive, weatherproof support structure, typically made of porcelain or polymer insulators


Replaceable Components of Drop-Out Fuses (DO Fuse
The Drop-Out Fuse (DOF) is a sacrificial device, meaning one part is deliberately designed to be consumed during a fault. Therefore, the primary and most frequently replaced part is the fusible element itself.
The critical spare components for a DO Fuse are:
• Fuse Element/Link: This is the heart of the device. It is a calibrated wire or strip designed to melt at a specific current level. Since the "drop-out" action is the result of this element melting, utility crews must carry a stock of appropriately rated fuse links (e.g., 10\text{A}, 20\text{A}, etc.) for every service restoration after a fault.
• Fuse Tube (Fuse Carrier): This tube, made of high-strength material like fiberglass or an insulating composite, houses the fuse link and the arc-quenching material. Although designed to withstand the internal explosion from arc extinction, repeated operations or severe faults can damage the tube, necessitating its replacement.
• Non-Ferrous Contacts: The contacts that hold the fuse tube in place (upper and lower fittings) are subjected to the heat and forces of the fuse operation and need to be in good condition to ensure a proper connection. These parts, often made of brass or copper, are replaced if they show signs of pitting, wear, or excessive corrosion.